A recent study highlights the potential challenges of scaling up organic farming and its impact on soil organic carbon (SOC) stocks. The study emphasizes the importance of implementing strategies like increased cover cropping to mitigate potential declines in SOC stocks.
The Potential Impact of Global Organic Farming Expansion on Soil Organic Carbon Stocks
Organic farming has gained significant attention as a potential solution to address the environmental challenges associated with conventional agriculture. With a focus on avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, organic farming practices have been shown to promote soil health and biodiversity. However, a recent study suggests that the expansion of organic farming may have unintended consequences for soil organic carbon (SOC) stocks.
( Credit to: Nature )
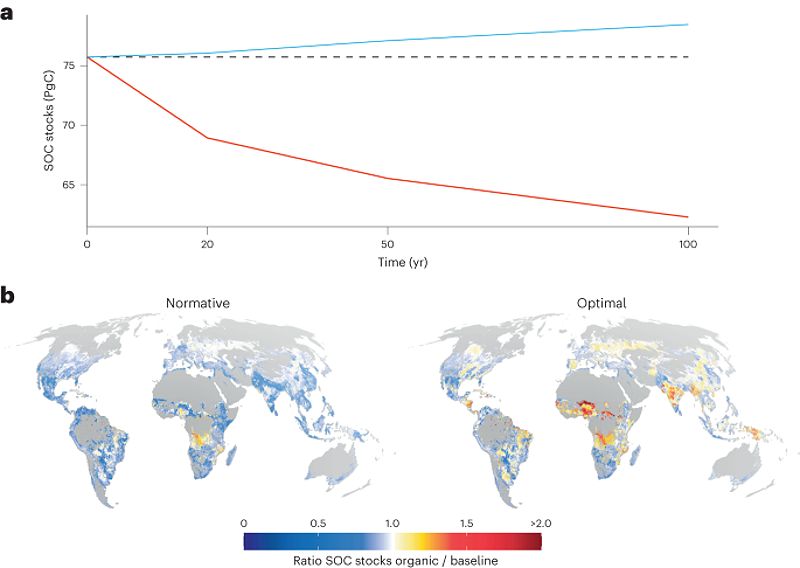
A team of researchers conducted a modeling approach to estimate the potential effect of globally expanding organic farming on cropland SOC stocks. The results indicate that large-scale expansion of organic farming could lead to a reduction in SOC stocks unless appropriate farming practices are adopted. This finding emphasizes the importance of implementing strategies like increased cover cropping to mitigate the potential decline.
The Importance of Soil Organic Carbon in Organic Farming
Soil organic carbon (SOC) is a crucial component of soil health and plays a vital role in mitigating climate change. It helps improve soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability. Organic farming practices, such as the use of organic amendments and reduced tillage, can enhance SOC stocks compared to conventional farming methods.
While previous studies have shown that organic farming has the potential to increase SOC stocks, the recent research suggests that large-scale expansion may pose challenges. One of the main limitations identified is the availability of nitrogen resources. Organic farming relies on natural sources of nitrogen, such as cover crops and organic fertilizers, which may not be sufficient to support widespread expansion.
Mitigating the Potential Decline in Soil Organic Carbon Stocks
The findings of the study have important implications for policymakers and farmers considering the expansion of organic farming. To maintain or even enhance SOC levels while scaling up organic farming, it is crucial to implement practices like cover cropping, crop rotation, and proper organic waste management. These strategies can help mitigate the potential decline in SOC stocks.
By adopting appropriate farming practices and ensuring the availability of necessary resources, we can maximize the benefits of organic farming while minimizing any potential negative consequences for soil health and climate change mitigation. Further research and collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and farmers are essential to develop strategies that promote sustainable and resilient agricultural systems.
