Learn about the new EU regulations on organic production and labeling that aim to improve the quality of organic food and farming in Europe. These regulations promote sustainable practices, environmental protection, and animal welfare, ensuring high standards across the supply chain.
- Understanding Organic Farming: Sustainable Practices for Quality Food
- The EU Organic Logo: A Guarantee of Organic Standards
- Expanding the Organic Market: Meeting the Growing Demand
- Preventing Contamination: Stricter Controls for Organic Production
- Improving Supply and Certification: Enhancing Organic Farming Practices
Understanding Organic Farming: Sustainable Practices for Quality Food
Organic farming is a sustainable agricultural system that prioritizes environmental protection and animal welfare. With the new EU regulations on organic production and labeling, the quality of organic food and farming in Europe is set to improve. As an expert in organic farming with over 15 years of experience, I’m here to guide you through the key aspects of organic farming and its benefits.

( Credit to: Europarl )
Organic farmers in the EU are committed to responsible resource utilization and promoting animal health. They employ practices like crop rotation to optimize resource utilization, ban chemical pesticides and synthetic fertilizers, and strictly limit livestock antibiotics. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are prohibited, and livestock is raised in free-range, open-air environments with organic fodder.

( Credit to: Europarl )
These sustainable practices not only contribute to biodiversity and ecological balance but also protect water and soil quality. By utilizing on-site resources for natural fertilizers and animal feed, organic farmers minimize their impact on the environment and ensure the production of high-quality organic food.
The EU Organic Logo: A Guarantee of Organic Standards
To guarantee that organic production rules are followed, the EU has introduced an organic logo that must be displayed on pre-packaged organic food products. This logo serves as a symbol of trust and ensures that consumers can identify genuine organic products.
( Credit to: Europarl )
In order to carry the organic logo, at least 95% of the ingredients of agricultural origin in processed food must be organic. Supermarkets and retailers can only label their products as organic if they comply with these strict rules. This ensures that consumers can make informed choices and have confidence in the organic products they purchase.
Expanding the Organic Market: Meeting the Growing Demand
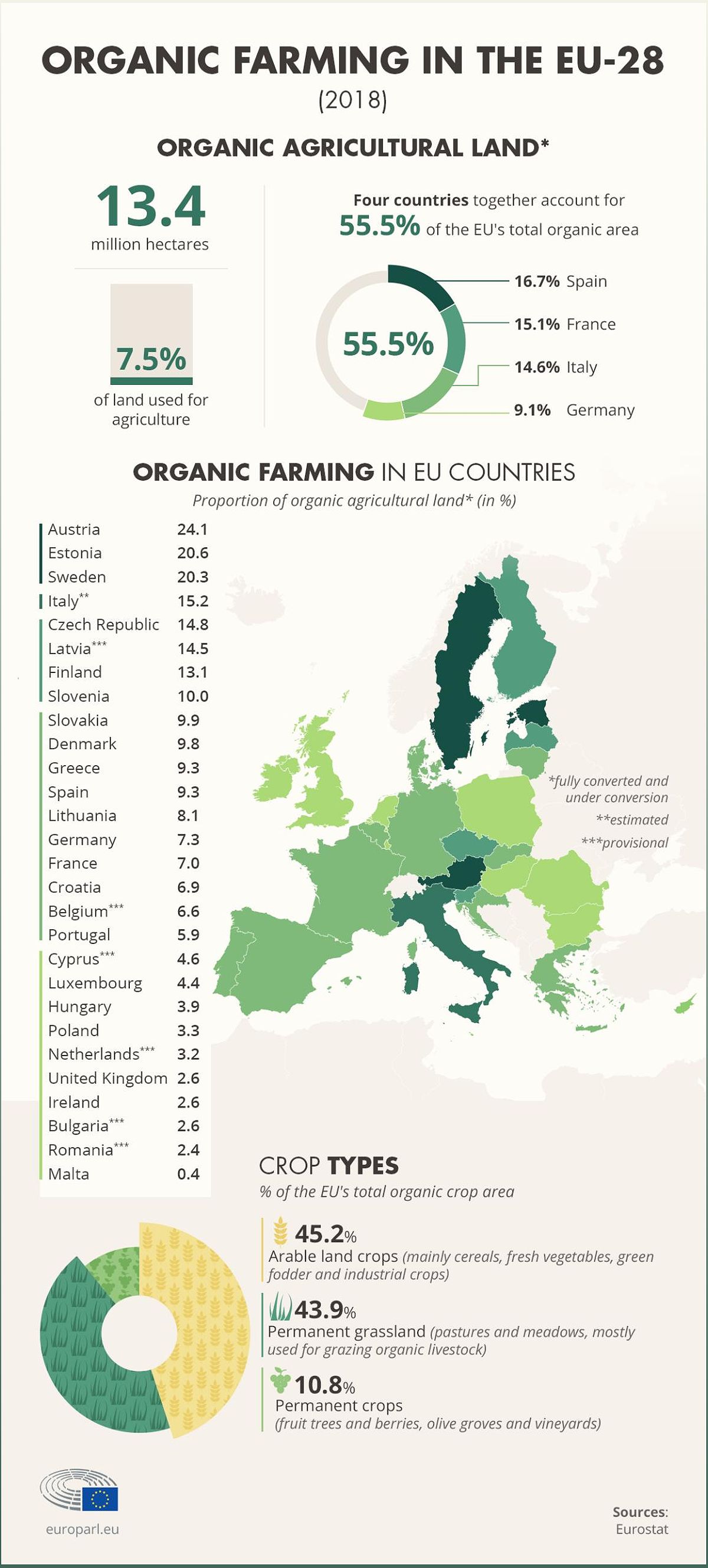
The organic market in the EU has been steadily expanding and is now worth approximately €37.4 billion per year. However, organic farmland still only accounts for 7.5% of the total agricultural area in the EU. To meet the growing demand for organic products, imports have increased.
In response to this changing landscape, the EU is updating its rules on organic production and labeling. These new regulations aim to ensure fair competition by requiring producers from non-EU countries to comply with the same rules as EU producers if they want to sell their products in the EU. This will maintain high standards across the board and provide consumers with a wider range of organic options.
Preventing Contamination: Stricter Controls for Organic Production
One of the focuses of the new EU regulations is to prevent contamination with pesticides. Farmers are now required to take precautionary measures to avoid accidental contamination with non-authorized pesticides or fertilizers. If contamination occurs due to fraud or negligence, the product loses its organic status.
EU countries that have thresholds for non-authorized substances in organic food can continue to apply them but must allow organic foods from other EU countries in their markets. This ensures that consumers are protected from contamination and can have confidence in the organic products they purchase.
The European Commission will also review the anti-contamination rules in 2025 to further enhance the prevention of contamination and maintain the integrity of organic production.
Improving Supply and Certification: Enhancing Organic Farming Practices
The new regulations also aim to improve the supply of organic seeds and animals by setting up a computer database on their availability in each EU country. This will ensure that organic farmers have access to high-quality organic seeds and animals for their farming practices.
Additionally, mixed farms are now allowed to produce conventional products alongside organic ones, as long as clear separation is maintained. This provides flexibility for farmers and allows them to adapt to market demands while upholding organic standards.
Certification procedures for small farmers are being simplified to encourage their participation in organic farming. This will help promote the growth of organic farming at a grassroots level and provide more diverse organic products for consumers.
With these new regulations, the EU is committed to enhancing the quality of organic food and farming in Europe. By ensuring sustainable practices, environmental protection, and animal welfare, the EU is meeting the growing demand for organic products while maintaining high standards across the supply chain.
